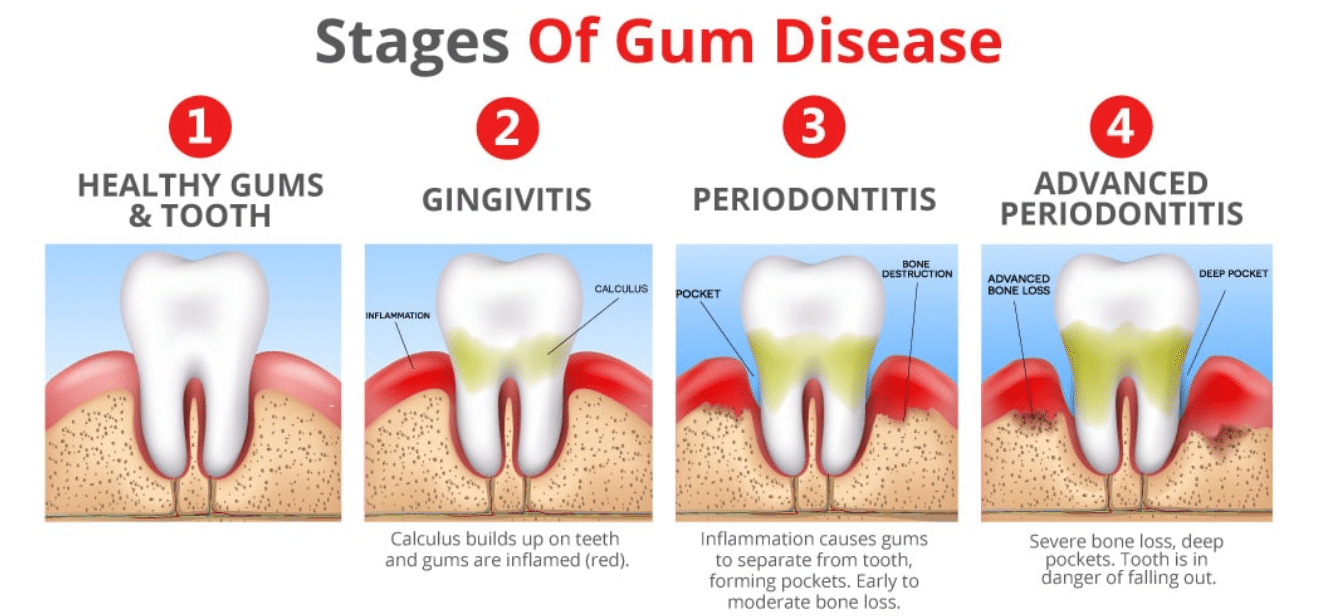
There are 3 main gum diseases: gingivitis, periodontitis, advanced periodontal disease. Let’s take a closer look at each of them.
Gingivitis – is inflammation of the gums, localized around one particular tooth and due to the negative influence of general and local factors. Basically, the disease develops against the background of improper oral hygiene. For pathogenic microbes, the nutrient medium is the appearance of plaque. Toxins secreted by microbes just provoke gum inflammation.
Periodontitis – inflammation of the teeth and gums, which is accompanied by the destruction of the supporting apparatus of the tooth, as well as the ligament between the bone and the root of
the tooth. The gum imperceptibly “moves away” from the tooth, creating a pocket where food accumulates. An unpleasant odor appears from the mouth, the teeth lose their durability, become loose, and if untreated, they fall out.
Advanced Periodontal disease – is a gum disease in which the blood supply to the tissues is disturbed, which leads to their complete degeneration, exposure of the neck of the teeth and an increase in the gaps between them. At the same time, the gum retains its normal color or becomes visibly pale, there is no bleeding. Since the development of the disease is not preceded by inflammatory processes, the patient consults a doctor even when the degenerative periodontal lesion has already affected both jaws.
The main causes of inflammation are:
- Microbes
- Inadequate or poor oral care
- the presence of tartar
- due to improper prosthetics and dental fillings
- smoking and vitamin deficiencies
- gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system diseases
Symptomatology
Symptoms of gum disease do not appear immediately. Only during oral hygiene can blood be
detected on the brush. Such moderate bleeding of the gums is considered the norm, so few people pay attention to this.
If no action is taken, obvious symptoms of the disease soon appear:
- pain, itching and burning
- redness and severe bleeding of the gums
- exposure of the necks of the teeth
- tooth sensitivity, pain reactions to food of different temperatures.
Treatment
Treatment of gum inflammation near the tooth should be comprehensive. Depending on the characteristics of the origin and development of the diesase, as well as the severity of changes in the tissues, an individual treatment plan is selected for the patient. It includes local treatment and general effects on the body.
To relieve gum inflammation, several tasks need to be addressed simultaneously:
- elimination of the focus of inflammation
- stopping and preventing relapses, complications
- preservation and restoration of the functions of the dentition.
Treatment of the inflammation of the pocket and gums under the prosthesis includes:
- Professional oral hygiene, which is carried out under local anesthesia
- antimicrobial and antiseptic treatment of the mouth
- removal and prevention of the appearance on the surface of the dentition of a microbial biofilm
- removal of hard and soft tooth deposits, polishing surfaces
- hygiene control and correction, mouth sanitation
- anti-inflammatory therapy and the appointment of vitamin complex.
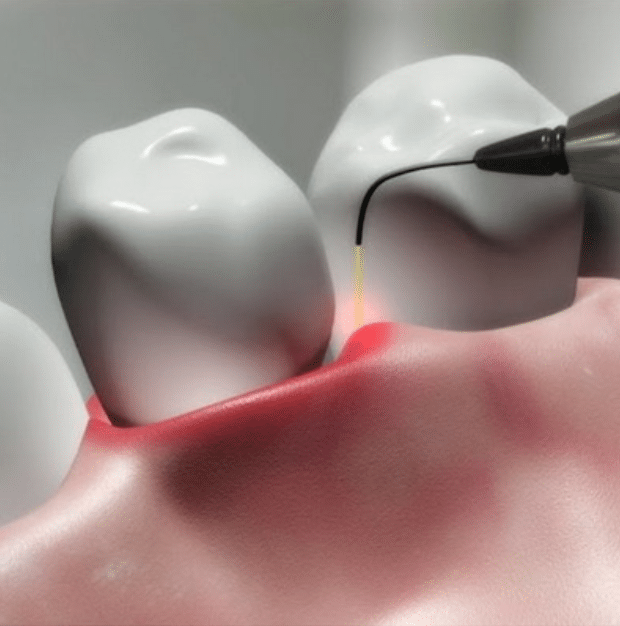
Besides all this, we can also offer laser treatment. This is one of the most common treatments we use for gum disease. The laser is absolutely painless, the procedure is faster and the patient does not feel discomfort.
Still have questions? Please contact us by phone 954-457-8308. We will be happy to discuss your concern and answer all your questions.